- Details
- Hits: 4288
Plastic packaging, films, and assorted plastic components will need careful attention to best use this waste stream to the greatest effect. Consequently incineration is not considered a viable solution due to problems with dioxins in the pollutant exhaust and poor levels of energy release.
 However many plastics are able to be re-formed into useful objects, in the storm water and management of flooding in many situations. One such use is of stable, underground water storage, both as flood control and for retention in hot climates - but suffering from short periods of heavy rains.
However many plastics are able to be re-formed into useful objects, in the storm water and management of flooding in many situations. One such use is of stable, underground water storage, both as flood control and for retention in hot climates - but suffering from short periods of heavy rains.
These interlocking forms can be stacked underground up to 5m in height - and still allow the land above to be used as playing fields or even for parking with appropriate additional strengthening. Very much ideal for nations where water/rainfall is for limited periodicity but heavy. Example West Coast of the African Continent, with trade winds bringing heavy rains.
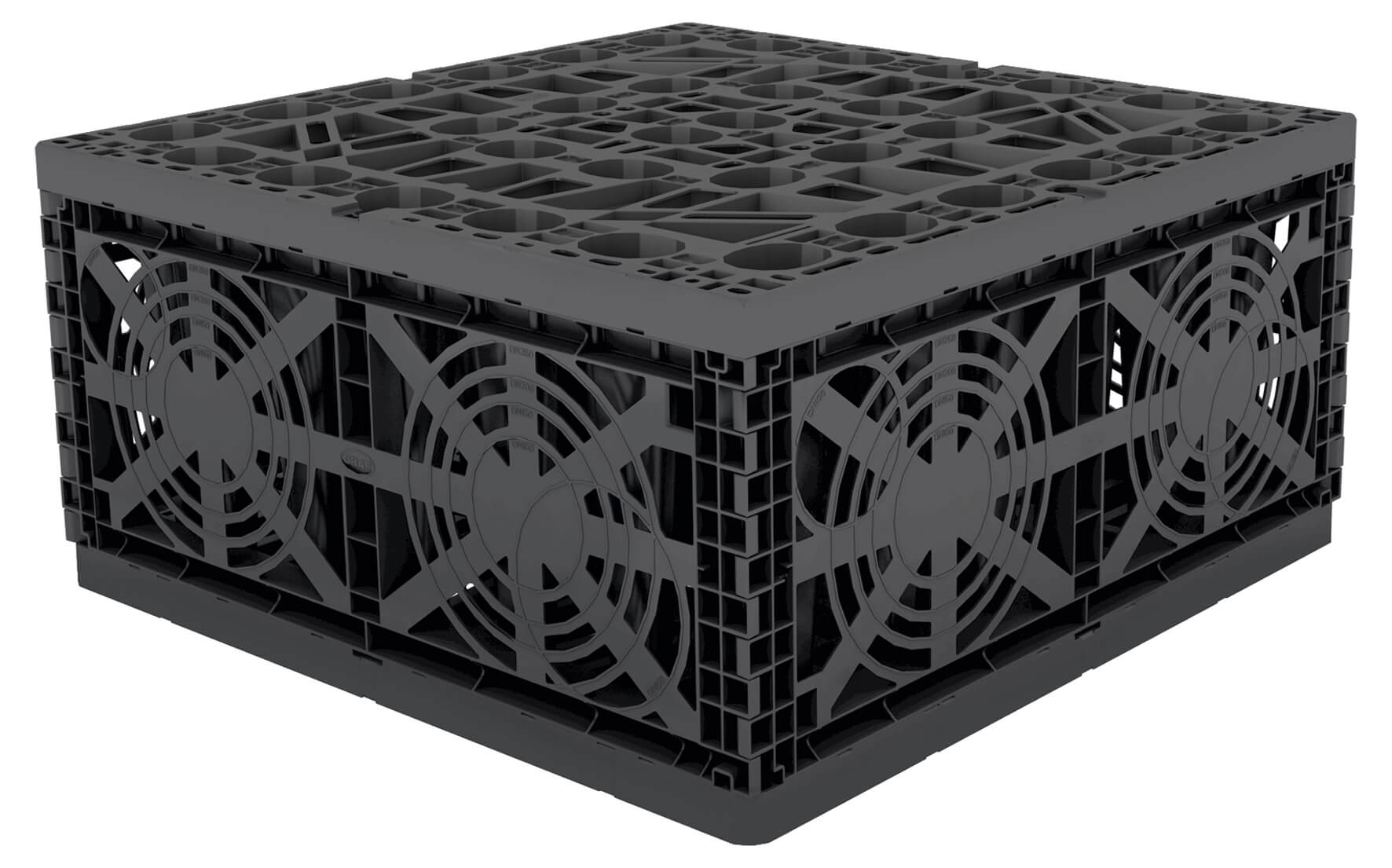
Stackable Plastic Crates
Stackable stormwater control crates offer a modular design that give you more flexibility over how the system is installed and set-up in the ground. One of the major benefits of using stackable crates is that the installation can be completed much faster and without the need to use specialist heavy equipment. These types of crates are more suitable for areas that cannot accommodate a long row of crates attached to each other. Instead, they are stacked on top of each other to retain a large storage holding and facilitate the release of rainwater into the surrounding environment when needed.
Light duty crates
Light duty stormwater control crates are best suited for pedestrian loads through to domestic vehicular loads. In most cases, light duty crates are installed in gardens and landscaping areas and have a load limit of around 20 tonnes. The depth of cover, tank depth, top surface cover, ground type (granular or cohesive) and usual loading traffic will all have to be accounted for to ensure this type of crate is suitable for the land.
Heavy duty crates
Heavy duty stormwater control crates are designed to accept large weight loads at ground level, often exceeding a 60-70 tonne load rating. The exact load a capacity is decided by the cover depth, soil type, surface finish and other similar factors, which can be determined by the installation company. A heavy-duty stormwater control crate is typically installed in areas that experience large amounts of traffic on a regular basis, or for car parking areas that accommodate several domestic vehicles.
- Details
- Hits: 3065
Key Situations:
Outline of the waste streams available that could be used for energy production - ideally bio-methane. However, plastics are today's "pollutants" to the viability of waste streams to energy. The plastic need a different method of treatment. Overall, we wish to avoid the less efficient {and problematic emissions} of incineration technologies.
WORK IN PROGRESS:
TYPES OF WASTE STREAMS |
|
 |
|
Homogeneous Organic Wastes, typically farming wastesThese typically farm based bio-digesters, can create good volumes of bio-methane [with some CO2 and other contaminants - which can be removed] from a wide variety of soft organic wastes - from cattle slurry to oil-rich seeds. We have a database of the energy values of most farm wastes to be able to estimate economic viabilities in terms of exporting to the gas grid, generating electricity and exporting to the electric grid or even as transport fuels {compressed natural gas} CNG. |
|
 |
|
Palm Oil Wastes and other industrial processesIn regions where Palm Oil production is prevalent, the waste lagoons associated with Palm Oil production, with the husks etc can be utilitise as rich source of bio-methane. The waste from these processes can be problematic in environmental terms - so bio-digestion is an ideal transformation into a commercial fuel or used in energy and heat production as a feed back into the industrial process itself. |
|
 |
|
Mixed Wastes and Rubbish TipsThere are a great many pre-existing waste tips of varying sizes and "conditions" globally - [Some tips can be on-fire or explosive with the methane generation]. Comprehensive treatment and separation of the leachate and methane can produce vast quantities of bio-methane [again with CO2, H2S etc - all of which can be separated]. The Leachate is also rich in Ammonia and other compounds. Experience in the UK shows that a waste tip can produce methane [and other smaller impurities] for up to 30 years. The London Brick Works in Bedfordshire used bio-methane from the waste tip on their clay pits {as supplied from London}, to fire their brick kilns for decades. |
|
 |
|
Plastic Waste "Pollution"The vastly increased usage of plastics over the last decades, has changed the composition of waste globally. Plastic themselves are difficult {not impossible} to break down and thus make bio-digestion more difficult. In practice the separation of Plastic {and metals, builders rubble etc} needs to be carried out before digestion. Other technologies to deal with plastics {see below} like Cold Plasma Pyrolysis can yield methane and Hydrogen. |
Anaerobic digestion can be used to generate energy from organic waste like food and animal products. In an oxygen-free tank, this material is broken down to biogas and fertiliser.
It’s an approach with big potential. If we treated 5.5 million tonnes of food waste this way, we’d generate enough energy to serve around 164,000 households while saving between 0.22 and 0.35 million tonnes of CO2, in comparison to composting.
Extracting the biogas produced by biodegrading materials on landfill sites is another way of getting useful energy from waste. Although it’s an approach that’s in decline due to the reduction of the amount of organic matter going to landfill, it’s making a notable contribution to UK energy supply: the source 3.04TWh of green electricity in the last year, in fact.
Tackling the plastic problem
Plastic waste has risen to significant levels of public consciousness in recent years, for its negative impact on habitats and species. In response, the UK Government’s 25-year Environment Plan pledges to eliminate all ‘avoidable’ plastic waste by the end of 2042 – and it’s not alone in making such political commitments. Can waste-to-energy step in here?
Converting plastic waste to energy certain makes sense from a chemical perspective, given plastics come from the same origin as fossil fuels. We’ve already looked at the two main techniques involved: pyrolysis, where plastic is heated in the absence of oxygen, and gasification, where air or steam heats the waste, creating gases that either produce petrol or diesel, or are burned to generate electricity.
New techniques such as cold plasma pyrolysis, provide the potential to create fuels such as hydrogen and methane, as well as useful chemicals for industry.
But there are barriers in the way of wider uptake of plastic-to-energy techniques. Gasification of plastics requires significant investment, including advanced controls and pre-treatment facilities. Also, developing plastic-recycling plants presents a risk of limiting those facilities, when decision-makers may instinctively opt for waste strategies where general waste is processed together, rather than separating out different elements.
Novel approaches to waste management in the UK will surely rise in the coming years. Recycling rates seem to be plateauing, with minor increases only seen. While generating energy from waste has a lot of promise, we need to focus on making products last longer, and when they really can’t be fixed, finding ways to recycle and reuse them. Only when those options are exhausted should we turn to waste-to-energy.
the prospect of using rubbish for fuel isn’t too far from reality. Plastics, in particular, contain mainly carbon and hydrogen, with similar energy content to conventional fuels such as diesel.
Plastics are among the most valuable waste materials – although with the way people discard them, you probably wouldn’t know it. It’s possible to convert all plastics directly into useful forms of energy and chemicals for industry, using a process called “cold plasma pyrolysis”.
Pyrolysis is a method of heating, which decomposes organic materials at temperatures between 400℃ and 650℃, in an environment with limited oxygen. Pyrolysis is normally used to generate energy in the form of heat, electricity or fuels, but it could be even more beneficial if cold plasma was incorporated into the process, to help recover other chemicals and materials.
The case for cold plasma pyrolysis
Cold plasma pyrolysis makes it possible to convert waste plastics into hydrogen, methane and ethylene. Both hydrogen and methane can be used as clean fuels, since they only produce minimal amounts of harmful compounds such as soot, un-burnt hydrocarbons and carbon dioxide (CO₂). And ethylene is the basic building block of most plastics used around the world today.
As it stands, 40% of waste plastic products in the US and 31% in the EU are sent to landfill. Plastic waste also makes up 10% to 13% of municipal solid waste. This wastage has huge detrimental impacts on oceans and other ecosystems.
- Details
- Hits: 2980
 Richard Blyth is the Head of Policy Practice and Research at the RTPI
Richard Blyth is the Head of Policy Practice and Research at the RTPI
There can be few in the planning world in England who are unaware of what I think it is fair to call a crisis over water quality. It goes by the tongue-twisting title of Nutrient Neutrality. Or you could say making sure that new development is net zero nitrate (or phosphate). To the best of my comprehension it began as a result of a European Court of Justice ruling (remember them?) in 2018 regarding the operation of the EU Habitats Directive (Remember that? Of course you do, it’s still in force). As a result Natural England began issuing directives of its own to local planning authorities, starting in the Solent area of Hampshire stating that no planning permissions for housing could be issued unless applicants could demonstrate that new housing would not add at all to the load of pollution coming out of sewage treatment works. One way of doing this is to create additional wetland habitat to replace the habitat damaged by ongoing pollution.
Anyone familiar with wetlands will soon appreciate that these priceless habitats take some time to be created – it is estimated five years. So mitigation – sorry eliminating – the impact of a single house is not easily achieved. Nevertheless with a lot of creative thinking on the part of local authorities in Hampshire and housebuilders a collective tariff based scheme was devised and it began operation around early 2019.
Sadly the progressive monitoring of Natural England has identified more and more habitats at risk from polluted water and more and more local planning authorities were told to stop granting planning permissions unless Natural England was satisfied about mitigation. First in the Somerset Levels, then in a lot of Herefordshire and Shropshire and parts of Kent. The count reached 74 planning authorities in March 2022, a kind of grand finale. (At least I hope it is a finale.) The Home Builders’ Federation estimates that about 100,000 homes are held up by this policy.
Those with long memories will recall this is not the first time we have had such a crisis. Threats to the Dartford Warbler and other nesting birds held up 40,000 homes around 2007 west of London while Natural England and housebuilders tried (eventually successfully) to find ways to allow people in new homes to walk their dogs without hurting wildlife.
The Government has listened to strong voices of concern from the RTPI, the HBF, the Construction Leadership Council and many others calling for resolution of this problem. In a response to a DEFRA consultation on environmental targets, the RTPI also called recently for more ambitious targets on farming pollution to be set for 2037 than DEFRA is proposing. It does seem strange that it is new housebuilding which is being held almost solely responsible for a problem which is due to both agricultural pollution and also existing sewage.
A Government press release last week proposed a new scheme with (as yet unknown) funding towards the improvement of water treatment works to unblock the flow of new permissions. The Government has also proposed a new “legal duty on water companies in England to upgrade wastewater treatment works by 2030 in ‘nutrient neutrality’ areas to the highest achievable technological levels”. However there has been no announcement regarding the contribution of agriculture.
It is clearly imperative that something is done quickly. The most critical casualties are small building firms dependent on being able to develop sites they have bought, as the Financial Times reported on 18 July (£). But inside the planning profession there are longer term issues. Where local plans depend on allocating land within (what is now deemed) critical river catchments, there is a concern that local plans will be held up for example in Shropshire and Greater Norwich. It seems like the last thing we need is slower local plans.
The RTPI believes that the current state of planning for the environment needs a shake up. We, along with the Broadway Initiative, have been developing the concept of local environment improvement plans (LEIPs) which would bring all the current plans for water, habitats, farming support, air quality and coastal management into a single whole. This would make the key task of aligning environmental plans and local plans a lot easier, which, for example, could mean that plans such as the Greater Cambridge local plan would have a guaranteed water supply to all sites. A starting point for LEIPs could be the Local Nature Recovery Strategies brought in by the Environment Act 2021.
There are so many reasons now why we cannot let environmental planning continue to be a side show. Drought, flood, heat waves, and even sea level rise are all needing long term solutions. And for public health reasons we now know just how important easy access to nature for our own species is - for all of us.
- Details
- Hits: 4341

The Anaerobic Digestion (AD) and biogas industry is recognised as one of the required quick fixes. The reasons are many:
- AD’s ability to mitigate methane emissions from rotting organic wastes, positions it among the ‘fastest, most immediate and cost-effective’ ways to solve the issues raised above - "low hanging fruit" as it were, and will play a crucial role in delivering the Global Methane Pledge.
- AD produces natural fertiliser, a ready organic replacement for its petro-chemical counterpart, where a 20% slump in supply, forecast to last for several years, has led to ‘famine’ warnings.
- AD produces renewable energy, that cuts costs of manufacture, allows governments to insulate economies from international price hikes.
- AD can produce biomethane as clean transport fuel – dramatically reducing so-called 'carbon (dioxide) emissions and cutting air pollution in our cities ( as a replacement of diesel fuels), delivering health benefits valued in the billions of dollars/pounds.
- AD and biogas are the readily available, ready to deploy at scale, solution to these global challenges. With the right enabling environment AD can deliver millions of skilled jobs, especially potentially transitioning from the oil and gas industry, rural sustainability, energy and food security.
- As a circular solution the deployment of AD has a ripple effect – stimulating sustainable practices across society. That is why the International Energy Agency (IEA) says AD sits at the heart of a circular economy and is the poster boy for net zero.
- AD sits at the heart of an integrated energy response to the challenges we face, delivering immediate results and ushering in an era of flexible energy management systems that integrates technologies across different energy vectors (electricity, heat and gas) and Supporting Food Production with the by-products (Compost etc).
Developing the enabling environment to unleash the power of biogas is what global thought leadership summit's explore, with industry leaders addressing best practice to de-risk and short-circuit AD deployment.
In summary: Some key features of bioenergy:
- Available now
- Applicable in all energy sectors (electricity, direct heat, transport)
- Readily integrated with existing infrastructure
- Store-able – it can support expansion of intermittent renewables
- It can deliver negative emissions when linked to Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS): BECCS / Bio-CCS
Bioenergy contributes to climate change mitigation when:
- Biomass is based on waste/residues
- Converted to energy products efficiently
- Used to displace GHG-intensive fuels
Bioenergy encompasses many potential feedstocks, conversion processes and energy applications. It interacts strongly with the agriculture, forestry and waste management sectors, and its prospects are linked to the growth of a broader bioeconomy. Bioenergy can only expand if supplied and used in a sustainable manner.
- Details
- Hits: 3311
The Palm Oil industry generates large quantity of wastes whose disposal is a challenging task. In the Palm Oil mill, fresh fruit bunches are sterilized after which the oil fruits can be removed from the branches. The empty fruit bunches (are left as residues, and the fruits are pressed in oil mills. The Palm Oil fruits are then pressed, and the kernel is separated from the press cake (mesocarp fibers). The palm kernels are then crushed and the kernels then transported and pressed in separate mills. In a typical Palm Oil plantation, almost 70% of the fresh fruit bunches are turned into wastes in the form of empty fruit bunches, fibers and shells, as well as liquid effluent. These by-products can be converted to value-added products or energy to generate additional profit for the Palm Oil Industry.
Palm Kernel Shells (PKS)
Palm kernel shells (or PKS) are the shell fractions left after the nut has been removed after crushing in the Palm Oil mill. Kernel shells are a fibrous material and can be easily handled in bulk directly from the product line to the end use. Large and small shell fractions are mixed with dust-like fractions and small fibres.
Moisture content in kernel shells is low compared to other biomass residues with different sources suggesting values between 11% and 13%. Palm kernel shells contain residues of Palm Oil, which accounts for its slightly higher heating value than average lignocelluloses Biomass. Compared to other residues from the industry, it is a good quality Biomass fuel with uniform size distribution, easy handling, easy crushing, and limited biological activity due to low moisture content.
Press fibre and shell generated by the Palm Oil mills are traditionally used as solid fuels for steam boilers. The steam generated is used to run turbines for electricity production. These two solid fuels alone are able to generate more than enough energy to meet the energy demands of a Palm Oil mill.
